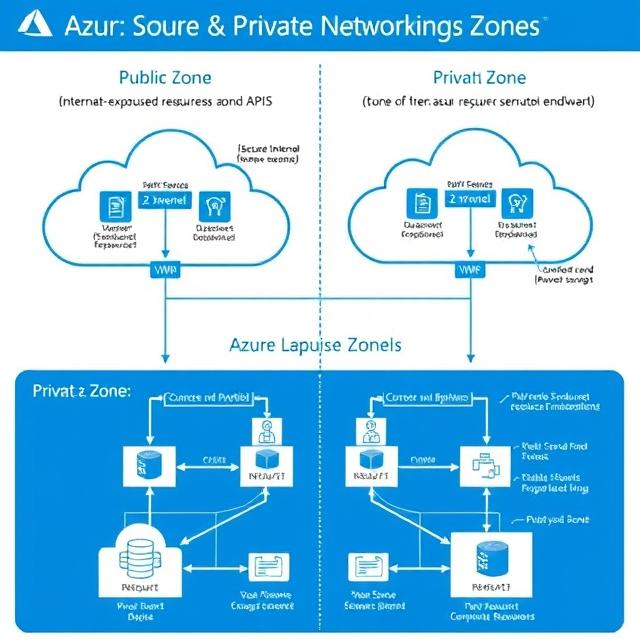
When you manage your cloud setup on Microsoft Azure, you need to understand public and private networking zones. These zones control how your resources talk to each other and to the outside world. In this post, we’ll explain the differences between public and private networking zones in Azure and when to use each one.
What Are Public and Private Networking Zones?
Networking zones in Azure group how traffic moves making sure resources can talk to each other and . Let’s look at them .
Public Networking Zones
Public networking zones are for resources that need to connect to the internet. These zones allow communication with people outside your network making them great for websites and APIs.
Key Characteristics:
- Internet Accessibility – Resources in public zones can be accessed from any place on the internet. Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) with public IPs are an example of this.
- Public IP Addresses – Resources that have public IPs (static or dynamic) can be reached from outside.
- Azure Services – Services like Azure App Service, Azure SQL Database (with public endpoint), and Azure Front Door are built to be accessible to the public.
- Security Measures – Public zones expose resources to outside traffic, but Azure offers security features to manage and protect them. These include Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Application Gateway with Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Private Networking Zones
Private networking zones make it easier for internal communication to happen within Azure or between Azure and on-premises networks. Resources in these zones don’t connect to the public internet, which boosts security and keeps things separate.
Key Characteristics:
- Internal Accessibility – You can reach resources inside an Azure Virtual Network (VNet) or through a VPN/ExpressRoute link.
- Private IP Addresses – Resources have private IPs that work within the Azure VNet making sure communication stays internal.
- Azure Services – Private networking options include Azure Virtual Network (VNet), Azure Private Link, and Azure Bastion, which let you access internal resources.
- Security Measures – You control access using VNet security settings, NSGs, and other Azure networking tools to protect internal resources.
When to Use Public and Private Networking Zones
Times to Choose Public Networking Zones:
- Web Applications – Websites and apps that need global access, like online stores, must sit in public zones.
- APIs – Public APIs for outside integrations and external partnerships need public accessibility.
- Public Services – Services that interact with the internet such as email services and social media integrations, use public zones.
When to Use Private Networking Zones:
- Internal Applications – HR, finance, and other sensitive apps should stay away from external exposure.
- Database Servers – Storing crucial business data in private zones makes sure only internal resources can access it.
- Hybrid Environments – Companies with on-site infrastructure can safely link their private networks to Azure using VPN or ExpressRoute.