Blockchain has a big impact on industries such as finance real estate, and even gaming. But as its popularity grows, the technology encounters major challenges — slow transactions high fees, and network congestion. To address these issues, developers created two types of solutions: Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains. Let’s break down what these layers mean in plain language.
What is a Layer 1 Blockchain?
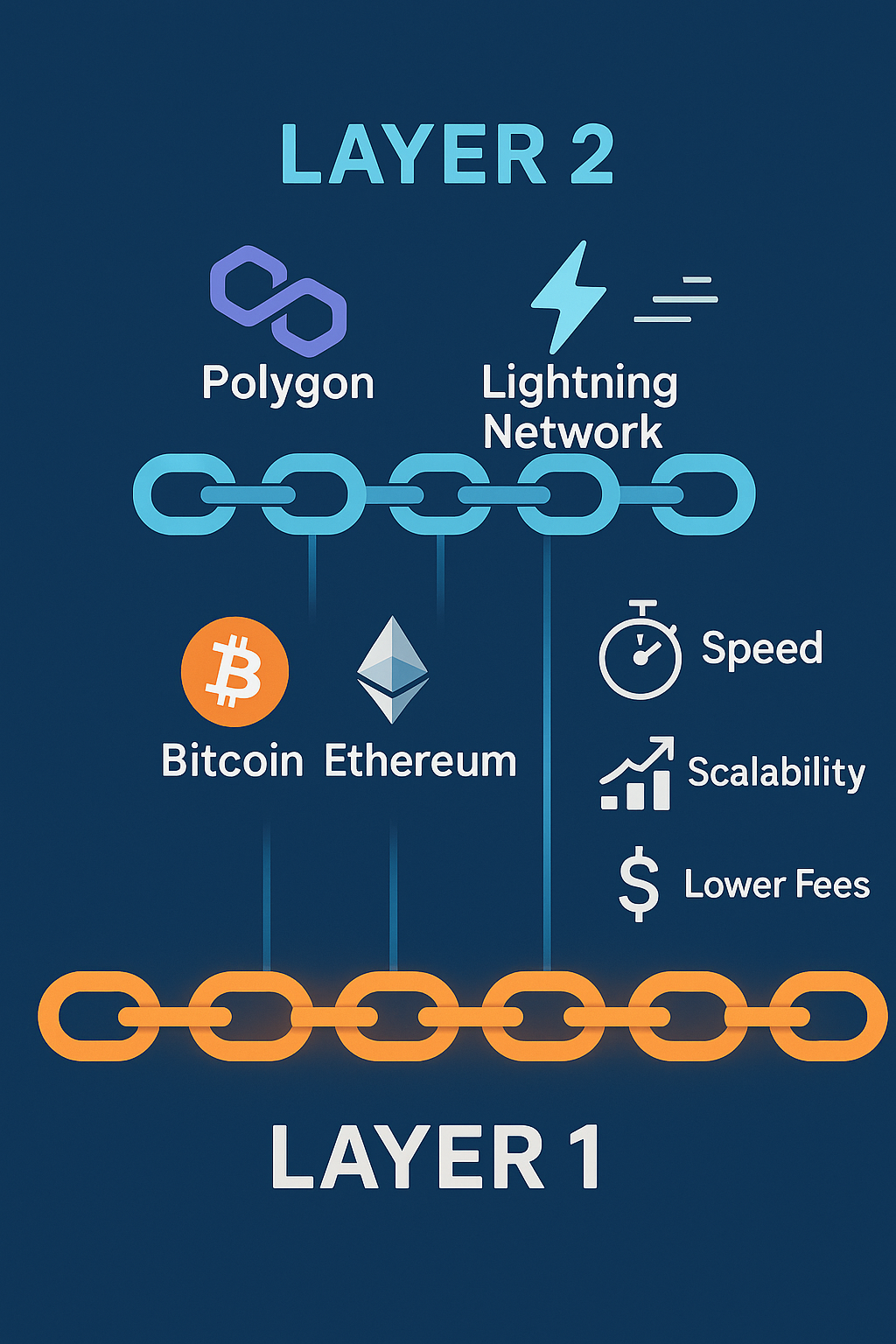
Layer 1 means the original blockchain network — the main platform where all transactions take place. It ensures the system stays secure, decentralized, and operational.
Some examples of Layer 1 blockchains include:
- Bitcoin (BTC)
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Solana (SOL)
These networks handle all transactions . They serve as the main roads for all traffic. But when too many transactions crowd the road, it slows down the network and raises fees.
Challenges Layer 1 Blockchains Face
Layer 1 blockchains pack a punch, but they have their limits:
- Scalability Issues: They can’t always cope with millions of users at once.
- Slow Speeds: Transactions might take minutes to confirm.
- High Costs: Busy networks force you to pay more to speed up your transaction.
What is a Layer 2 Blockchain?
Layer 2 serves as an extra structure on top of a Layer 1 blockchain. It processes transactions on its own and then logs the outcomes back on the main blockchain.
Picture Layer 2 as a quick side street next to the main highway. It cuts down traffic on the main road and helps cars zip along faster.
Well-known Layer 2 answers include:
- Polygon (teams up with Ethereum)
- Lightning Network (created for Bitcoin)
- Arbitrum (backs Ethereum)
How Layer 2 Improves Blockchain
- Quicker Transactions: Off-chain processing speeds up most of the work.
- Reduced Fees: Less network congestion leads to lower costs.
- Enhanced Scalability: The main network handles millions of transactions without strain.
Simple Example to Grasp
Picture a crowded coffee shop (Layer 1). Weekend lines stretch long for coffee orders. Now imagine a quick-order counter (Layer 2) where you place and pay for your order fast then the main counter just hands you your coffee. This shows how Layer 2 solutions help!
The Teamwork of Layer 1 and Layer 2
Layer 1 blockchains provide the bedrock of trust, security, and decentralization. Layer 2 solutions boost speed and productivity. They don’t compete — they work together to create a stronger, quicker blockchain ecosystem.